JavaScript
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a scripting or programming language that allows you to implement complex features on web pages, every time a web page does more than just sit there and display static information for you to look at displaying timely content updates, interactive maps, animated 2D/3D graphics, scrolling video jukeboxes, etc. you can bet that JavaScript is probably involved. It is the third layer of the layer cake of standard web technologies, two of which (HTML and CSS).
Examples of JavaScript is the browser:
- Slideshows.
- Forms.
- Reload part of page.
- Filtering data.
Scripts
- A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow to achieve a goal.
Writing a script
-
To write a script, you need to first state your goal and then list the tasks that need to be completed in order to achieve it, start with the big picture of what you want to achieve, and break that down into smaller steps.
-
Define the goal:
First, you need to define the task you want to achieve.
- Design the script:
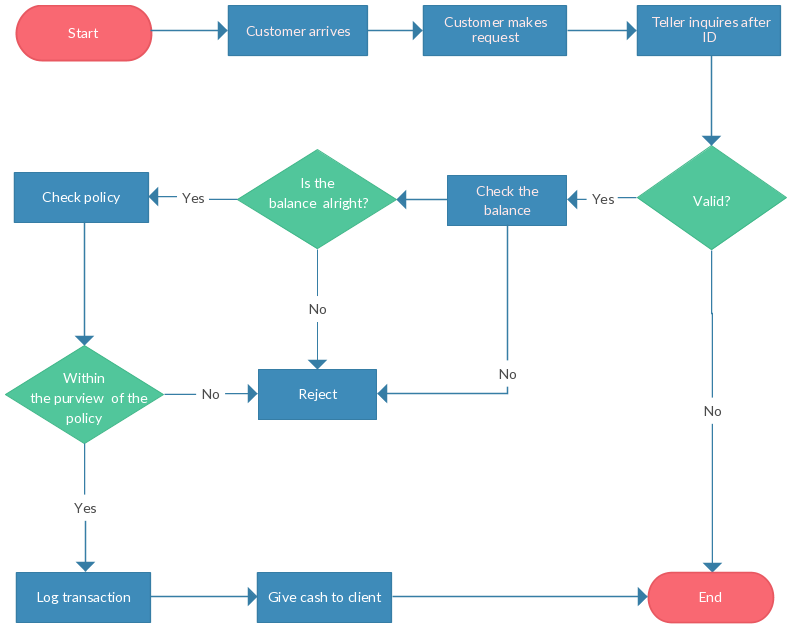
To design a script you split the goal out into a series of tasks that are going to be involved in solving this puzzle. This can be represented using a flowchart. You can then write down individual steps that the computer needs to perform in order to complete each individual task (and any information it needs to perform the task), rather like writing a recipe that it can follow.
-
Code each step:
- Each of the steps needs to be written in a programming language that the computer understands. In this case, it is JavaScript.
- As tempting as it can be to start coding straight away, it pays to spend time designing your script before you start writing it.
Flowchart example:
Variables
Rules for naming variables:
-
The name must begin with a letter, dollar sign ($),or an underscore (_). It must not start with a number.
-
The name can contain letters, numbers, dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_). Note that you must not use a dash(-) or a period (.) in a variable name.
-
You cannot use keywords or reserved words. Keywords are special words that tell the interpreter to do something. For example, var is a keyword used to declare a variable. Reserved words are ones that may be used in a future version of JavaScript.
-
All variables are case sensitive, so score and Score* would be different variable names, but it is bad practice to create two variables that have the same name using different cases.
-
Use a name that describes the kind of information that the variable stores. For example, firstName might be used to store a person’s first name, lastNarne for their last name, and age for their age.
-
If your variable name is made up of more than one word, use a capital letter for the first letter of every word after the first word. For example, firstName rather than firstname* (this is referred to as camel case). You can also use an underscore between each word (you cannot use a dash).
Arrays
- An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values.
Examples:
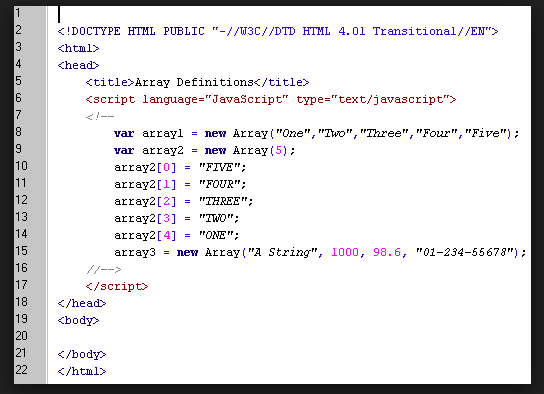
- The example below shows a 2 ways to create an array using JavaScript :
- The example below shows more actions you can do with arrays:

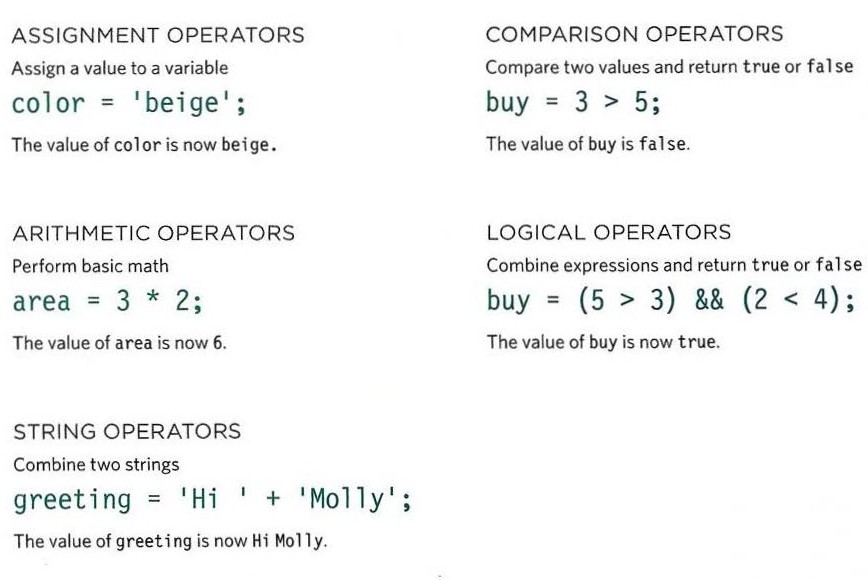
EXPRESSIONS
- An expression evaluates into (results in) a single value. Broadly speaking there are two types of expressions.
- Expressions that just assign a value to a variable.
Example:
var color = 'beige';
- The value of co1or is now beige.
- Expressions that use two or more values to return a single value.
Example:
var area = 3 * 2;
- The value of area is now 6.
Operators
- Expressions rely on things called operators; they allow programmers to create a single value from one or more values.
Example:
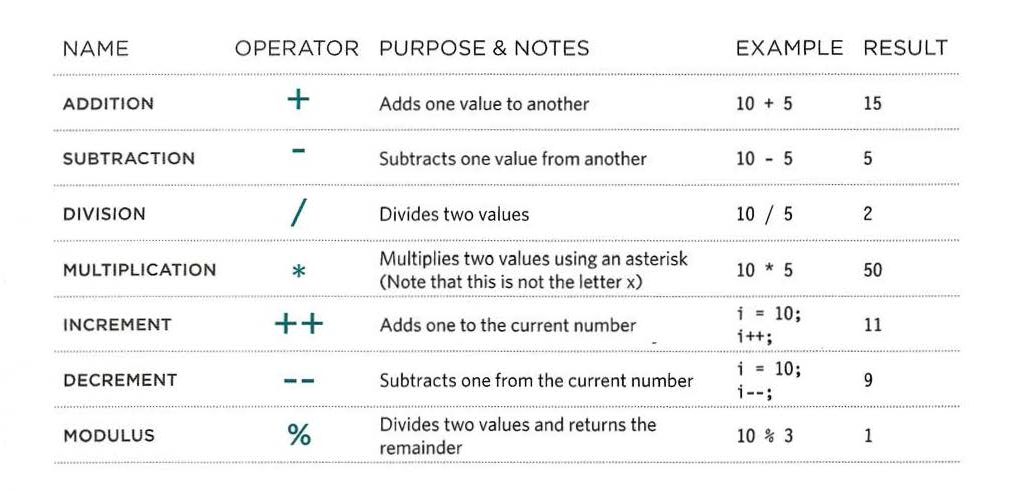
Arithmetic operators example:
Functions
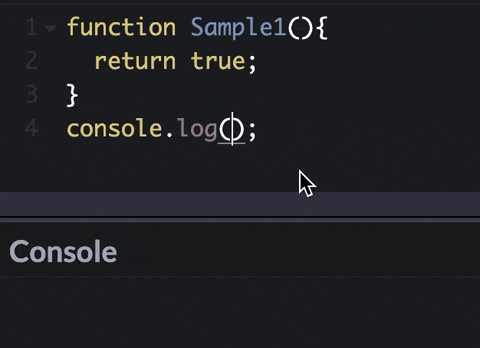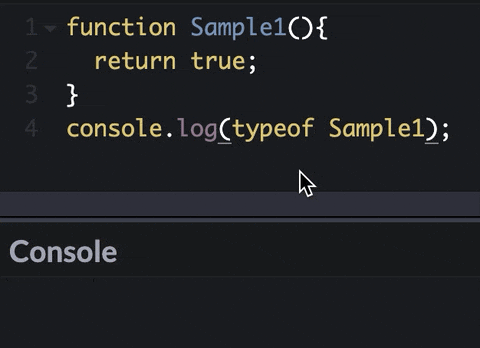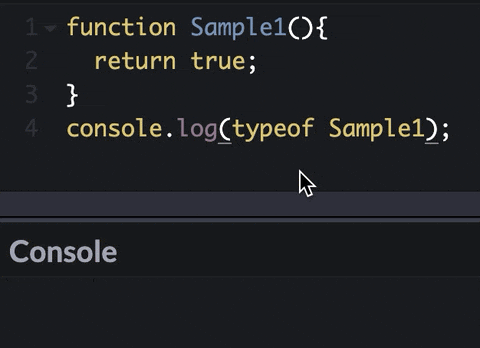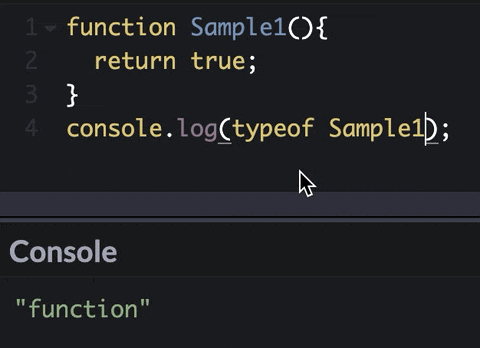
What is a function?
-
Functions let you group a series of statements together to perform a specific task.
-
Function declaration:

-
Calling a function:

-
Declaring functions that needs information

References:
- JavaScript and JQuery: Interactive Front-End Web Development by Jon Duckett Get the book