HTML & CSS

Chapter 5: Images
- There are many reasons why you might want to add an image to a web page: you might want to include a logo, photograph, illustration, diagram, or chart.
Adding Images
- <img>
To add an image into the page you need to use an <img> element. This is an empty element (which means there is no closing tag). It must carry the following two attributes:
-
src: This tells the browser where it can find the image file. This will usually be a relative URL pointing to an image on your own site.
-
alt: This provides a text description of the image which describes the image if you cannot see it.
-
title: You can also use the title attribute with the <img> element to provide additional information about the image. Most browsers will display the content of this attribute in a tootip when the user hovers over the image.
Where to Place Image in Your Code
-
Before a paragraph: The paragraph starts on a new line after the image.
-
Inside the start of a paragraph: The first row of text aligns with the bottom of the image.
-
In the middle of a paragraph: The image is placed between the words of the paragraph that it appears in.
Example:


Old Code: Aligning Images Horizontally
-
left: This aligns the image to the left (allowing text to flow around its right-hand side).
-
right: This aligns the image to the right (allowing text to flow around its left-hand side).


Old Code: Aligning Images Vertically
-
top: This aligns the first line of the surrounding text with the top of the image.
-
middle: This aligns the first line of the surrounding text with the middle of the image.
-
bottom: This aligns the first line of the surrounding text with the bottom of the image.


Cropping Images
- When cropping images it is important not to lose valuable information. It is best to source images that are the correct shape if possible.

Image Resolution
-
Images created for the web should be saved at a resolution of 72 ppi. The higher the resolution of the image, the larger the size of the file.
-
PGs, GIFs, and PNGs belong to a type of image format known as bitmap. They are made up of lots of miniature squares. The resolution of an image is the number of squares that fit within a 1 inch x 1 inch square area.
-
Images appearing on computer screens are made of tiny squares called pixels. The web browsers on most desktop computers display images at a resolution of 72 pixels per inch (ppi). Images in print materials (such as books and magazines) are made up of tiny circles called dots. These images are usually printed at a resolution of 300 dots per inch (dpi).
Vector Images
- Vector images differ from bitmap images and are resolution-independent. Vector images are commonly created in programs such as Adobe Illustrator.
When an image is a line drawing (such as a logo, illustration, or diagram), designers will often create it in vector format.
Vector formatted images are very different to bitmap images. Vector images are created by placing points on a grid, and drawing lines between those points. A color can then be added to “fill in” the lines that have been created.
The advantage of creating line drawings in vector format is that you can increase the dimensions of the image without affecting the quality of it.
Animated GIFs
-
Animated GIFs show several frames of an image in sequence and therefore can be used to create simple animations.
-
Because GIFs are not an ideal format for displaying photographs, animated GIFs are really only suitable for simple illustrations.
-
Some designers frown on animated GIFs because they remember a lot of amateur web designers overusing them in the 1990’s.
Chapter 11: Color
-
The color property allows you to specify the color of text inside an element. You can specify any color in CSS in one of three ways:
-
RGB values: These express colors in terms of how much red, green and blue are used to make it up. For example: rgb(100,100,90)
-
Hex code: These are six-digit codes that represent the amount of red, green and blue in a color, preceded by a pound or hash # sign. For example: #ee3e80.
-
Color names: There are 147 predefined color names that are recognized by browsers. For example: DarkCyan.

Understanding Color
Every color on a computer screen is created by mixing amounts of red, green, and blue. To find the color you want, you can use a color picker.


Contrast
When picking foreground and background colors, it is important to ensure that there is enough contrast for the text to be legible.

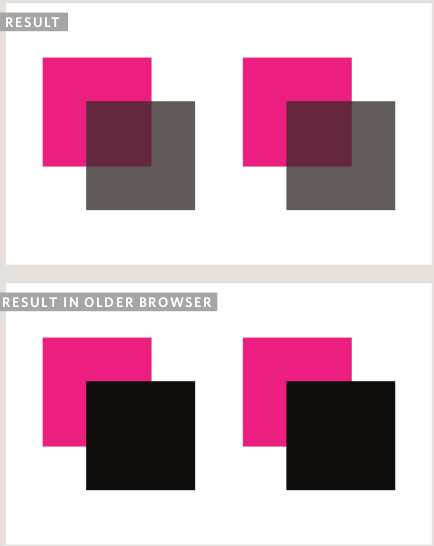
Opacity
Example:
p.one {
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
opacity: 0.5;}
p.two {
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.5);}
HSL Colors
CSS3 introduces an entirely new and intuitive way to specify colors using hue, saturation, and lightness values.

Chapter 12: Text
The properties that allow you to control the appearance of text can be split into two groups:
-
Those that directly affect the font and its appearance (including the typeface, whether it is regular, bold or italic, and the size of the text).
-
Those that would have the same effect on text no matter what font you were using (including the color of text and the spacing between words and letters).
- The formatting of your text can have a significant effect on how readable your pages are. As we look through these properties I will also give you some design tips on how to display your type.




Specifying Typefaces
font-family
-
The font-family property allows you to specify the typeface that should be used for any text inside the element(s) to which a CSS rule applies.
-
The value of this property is the name of the typeface you want to use.


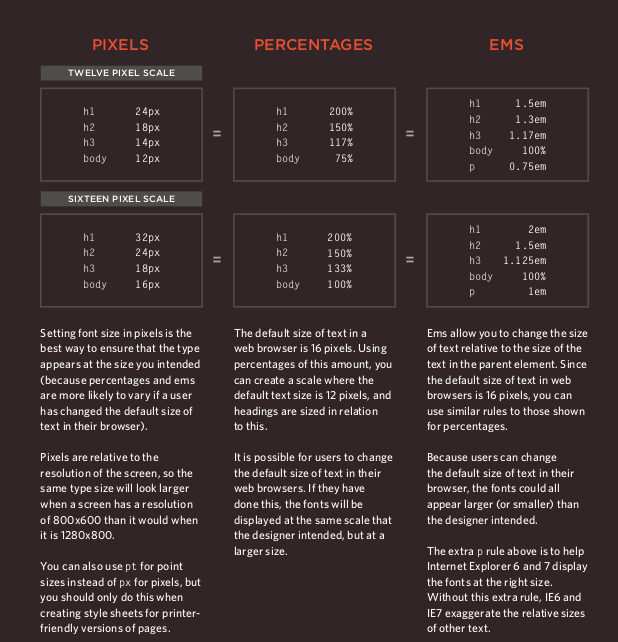
Units of Type Size
UpperCase & LowerCase
text-transform
- The text-transform property is used to change the case of text giving it one of the following values:
-
uppercase:This causes the text to appear uppercase.
-
lowercase: This causes the text to appear lowercase.
-
capitalize: This causes the first letter of each word to appear capitalized.

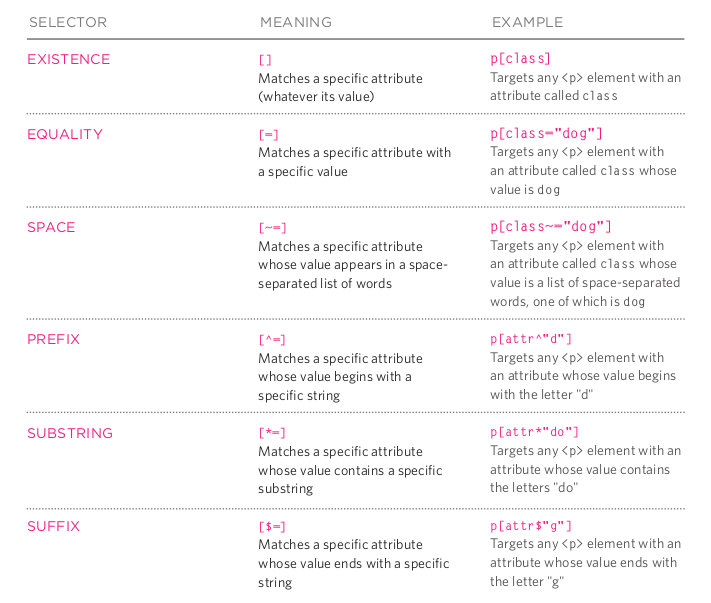
Attribute Selectors
Article Summary: JPEG vs PNG vs GIF — which image format to use and when?
When to use each image format?
- Use JPEG format for all images that contain a natural scene or photograph where variation in colour and intensity is smooth.
- Use PNG format for any image that needs transparency or for images with text & objects with sharp contrast edges like logos.
- Use GIF format for images that contain animations.
Compression
- Compression can be of two types:
- lossless, like PNG and GIF.
- lossy, like JPEG.
Transparency
In a simple form, transparency indicates something that is completely invisible. Logos and icons often need to be placed on backgrounds with variable colours. Hence it is desirable, that the background of these logos and icons is made transparent so that a single image can be used over multiple background variations.
-
JPEG images don’t support transparency and are hence not usable for such cases.
-
PNG images support transparency.
-
GIF images support transparency by declaring a single colour in the colour palette as transparent (index transparency).
References:
-
HTML & CSS Design and Build Websites by Jon Duckett Get the book
-
JPEG vs PNG vs GIF Read the full article here