HTML

Chapter 3: Lists
- HTML provides us with three different types of lists:
-
Ordered lists are lists where each item in the list is numbered. For example, the list might be a set of steps for a recipe that must be performed in order, or a legal contract where each point needs to be identified by a section number.
-
Unordered lists are lists that begin with a bullet point (rather than characters that indicate order).
-
Definition lists are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
Ordered Lists
-
The ordered list is created with the ol element.
-
Each item in the list is placed between an opening li tag and a closing li tag. (The li stands for list item.)
Ordered List Example:
<ol>
<li>Chop potatoes into quarters</li>
<li>Simmer in salted water for 15-20 minutes until tender</li>
<li>Heat milk, butter and nutmeg</li>
<li>Drain potatoes and mash</li>
<li>Mix in the milk mixture</li>
</ol>

Unordered Lists
-
The unordered list is created with the ul element.
-
Each item in the list is placed between an opening li tag and a closing li tag. (The li stands for list item.)
Unordered List Example:
<ul>
<li>1kg King Edward potatoes</li>
<li>100ml milk</li>
<li>50g salted butter</li>
<li>Freshly grated nutmeg</li>
<li>Salt and pepper to taste</li>
</ul>

Definition Lists
References:
-
The definition list is created with the dl element and usually consists of a series of terms and their definitions. Inside the dl element you will usually see pairs of dt and dd elements.
-
dt tag: This is used to contain the term being defined (the definition term).
-
dd tag: This is used to contain the definition. Sometimes you might see a list where there are two terms used for the same definition or two different definitions for the same term.
Definition List Example:
<dl>
<dt>Sashimi</dt>
<dd>Sliced raw fish that is served with condiments such as shredded daikon radish or ginger root, wasabi and soy sauce</dd>
<dt>Scale</dt>
<dd>A device used to accurately measure the weight of ingredients</dd>
<dd>A technique by which the scales are removed from the skin of a fish</dd>
<dt>Scamorze</dt>
<dt>Scamorzo</dt>
<dd>An Italian cheese usually made from whole cow's milk (although it was traditionally made from buffalo milk)</dd>
</dl>


Chapter 13: Boxes
Box Dimensions (width, height)
-
By default a box is sized just big enough to hold its contents. To set your own dimensions for a box you can use the height and width properties.
-
The most popular ways to specify the size of a box are to use pixels, percentages, or ems. Traditionally, pixels have been the most popular method because they allow designers to accurately control their size.
-
When you use percentages, the size of the box is relative to the size of the browser window or, if the box is encased within another box, it is a percentage of the size of the containing box.
-
When you use ems, the size of the box is based on the size of text within it. Designers have recently started to use percentages and ems more for measurements as they try to create designs that are flexible across devices which have different-sized screens.
Example:

Limiting width and height
-
width:
-
Some page designs expand and shrink to fit the size of the user’s screen. In such designs, the min-width property specifies the smallest size a box can be displayed at when the browser window is narrow, and the max-width property indicates the maximum width a box can stretch to when the browser window is wide.
-
These are very helpful properties to ensure that the content of pages are legible (especially on the smaller screens of handheld devices).
-
For example, you can use the max-width property to ensure that lines of text do not appear too wide within a big browser window and you can use the min-width property to make sure that they do not appear too narrow.
Width Example:

-
height:
-
In the same way that you might want to limit the width of a box on a page, you may also want to limit the height of it. This is achieved using the min-height and max-height properties.
-
If the box is not big enough to hold the content, and the content expands outside the box it can look very messy. To control what happens when there is not enough space for the content of a box, you can use the overflow property, which is discussed on the next page.
Height Example:

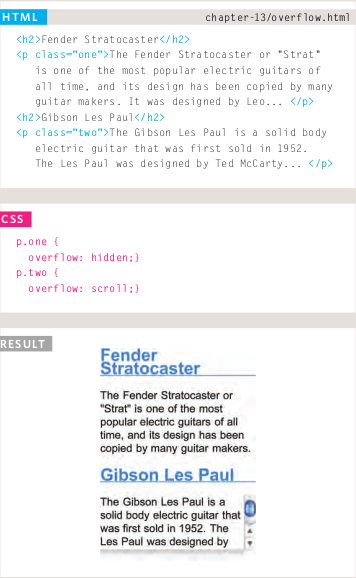
Overflowing Content
overflow:
The overflow property tells the browser what to do if the content contained within a box is larger than the box itself. It can have one of two values:
- hidden:
This property simply hides any extra content that does not fit in the box.
- scroll
This property adds a scrollbar to the box so that users can scroll to see the missing content. This property simply hides any extra content that does not fit in the box.
Overflow Example:
Border, Margin & Padding
- Every box has three available properties that can be adjusted to control its appearance:

White space & Vertical Margin
- The padding and margin properties are very helpful in adding space between various items on the page.

- Designers refer to the space between items on a page as white space. Imagine you had a border around a box. You would not want the text to touch this border or it would become harder to read.
JavasCript

Chapter 2: Basic JavaScript Instructions
How to use objects and methods

- When the browser comes across a script element, it stops to load the script and then checks to see if it needs to do anything.
Chapter 4: Decisions and Loops” from switch statements
Decisions And Loops
Comparison Operators
Evaluating Conditions


Using comparision operators
Example:
var pass = 50; // Pass mark
var score = 90; //Score
// Check if the user has passed
var hasPassed = score > = pass ;
// Write the message into the page
var el = document.getElementByl('answer');
e1.textContent = 'Leve 1 passed: ' + hasPassed;
If Statment

If Else Statment

Loops
-
Loops check a condition. If it returns true,a code block will run. Then the condition will be checked again and if it still returns true, the code block will run again. it repeats until the condition returns 2false.
-
There are 3 common tyoes of loops :

Loop counters and For Loops

Using While loops
While Example:

Using Do While loops
Do While Example:

Using Switch Statements



References:
-
HTML & CSS Design and Build Websites by Jon Duckett Get the book
-
JavaScript and JQuery: Interactive Front-End Web Development by Jon Duckett Get the book